
Table of Contents
Bursitis is one of those conditions that can sneak up on you, turning simple movements into painful experiences. But what exactly is bursitis, and why should you care? Whether you’re dealing with it yourself or know someone who is, understanding bursitis is key to managing it effectively.
Understanding Bursitis
Definition of Bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of a bursa, which is a small fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissues like muscles, tendons or skin. Think of a bursa as a little pillow that reduces friction and helps your joints move smoothly.
Anatomy of a Bursa
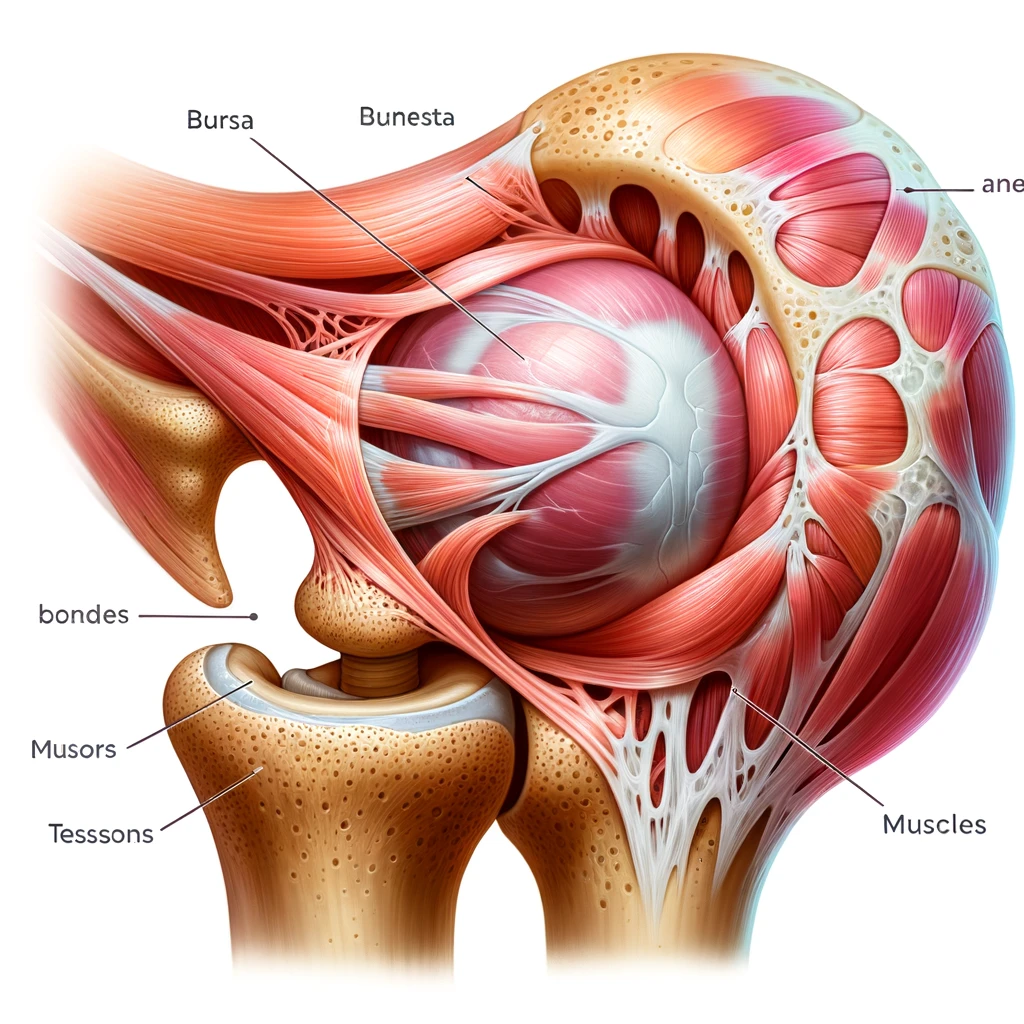
There are more than 150 bursae in your body, strategically placed around major joints such as the shoulders, elbows, hips and knees. Each bursa is like a mini shock absorber, protecting your joints and making sure everything glides smoothly.
Common Types of Bursitis
- Shoulder Bursitis: Often caused by repetitive overhead activities.
- Elbow Bursitis: Known as “student’s elbow” or “miner’s elbow,” often due to prolonged leaning on the elbows.
- Hip Bursitis: Common in runners or those with improper posture.
- Knee Bursitis: Also called “housemaid’s knee,” typically from kneeling for long periods.
Causes of Bursitis
Repetitive Motion
Repetitive activities, whether at work or play, can cause bursae to become inflamed. Think of actions like painting, gardening or playing a musical instrument.
Prolonged Pressure
Prolonged pressure on a joint, like kneeling or leaning on elbows, can irritate a bursa. It’s like pressing down on a cushion repeatedly; eventually, it gets flattened and damaged.
Traumatic Injury
A sudden impact or fall can cause bursitis, leading to immediate inflammation and pain.
Inflammatory Conditions
Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout can also lead to bursitis, as these diseases cause overall inflammation in the body.
Symptoms of Bursitis
Pain
Pain is the most common symptom, often sharp and intense, especially when moving the affected joint.
Swelling
Swelling around the joint is typical, as the inflamed bursa fills with excess fluid.
Redness
Redness and warmth over the area of the bursa can indicate inflammation or infection.
Limited Range of Motion
Movement can become restricted due to pain and swelling, making everyday activities difficult.
Diagnosing Bursitis
Physical Examination
A doctor will typically start with a physical exam, checking for tenderness, swelling and range of motion.
Medical History
Discussing your symptoms, activities and any previous injuries helps in pinpointing the cause of bursitis.
Imaging Tests
X-rays, MRIs or ultrasounds might be used to rule out other conditions and confirm bursitis.
Treatment Options
Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the affected joint and avoiding activities that worsen the symptoms is crucial. This might mean taking a break from sports or modifying work tasks.
Ice and Heat Therapy
Applying ice packs can reduce swelling and pain, while heat packs can help relax muscles and increase blood flow.
Medications
Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, a doctor might prescribe stronger medications.
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen muscles around the joint, improving flexibility and reducing the risk of recurrence.
Injections
Corticosteroid injections can provide quick relief by reducing inflammation. However, they’re not a long-term solution.
Surgery
In rare cases, when other treatments fail, surgery might be necessary to remove the inflamed bursa.
Home Remedies for Bursitis
R.I.C.E. Method
Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (R.I.C.E) is a standard approach to managing minor injuries and can be effective for bursitis as well.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Gentle Exercises and Stretches
Stretching and gentle exercises can improve flexibility and strength, helping to prevent further flare-ups.
Using Proper Equipment and Techniques
Whether it’s the right shoes or ergonomic tools, using proper equipment can make a big difference in preventing bursitis.
Preventing Bursitis
Ergonomic Adjustments
Adjust your workspace to reduce strain on your joints. This might mean changing the height of your chair or using a supportive cushion.
Regular Exercise
Regular exercise can help keep your joints flexible and muscles strong, reducing the risk of bursitis.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on your joints, particularly those in the lower body.
Protective Gear
Using knee pads, elbow pads, or other protective gear during activities can help prevent bursitis.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Bursitis
Balanced Diet
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables and omega-3 fatty acids can help manage symptoms.
Adequate Hydration
Staying hydrated helps keep your joints lubricated and functioning properly.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate pain and inflammation, so finding ways to manage stress, like through meditation or yoga, can be beneficial.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent Symptoms
If symptoms persist despite home treatment, it’s time to see a doctor.
Severe Pain
Severe pain that limits your daily activities needs professional attention.
Signs of Infection
Redness, warmth, and fever along with bursitis symptoms could indicate an infection, requiring prompt medical treatment.
Complications of Untreated Bursitis
Chronic Pain
Ignoring bursitis can lead to chronic pain, which can be debilitating.
Limited Mobility
Untreated bursitis can cause lasting damage, leading to permanent loss of mobility in the affected joint.
Bursa Infection
An untreated inflamed bursa can become infected, a condition known as septic bursitis, which can be serious.
Living with Chronic Bursitis
Coping Strategies
Learning to manage chronic bursitis involves coping strategies like pacing your activities and knowing your limits.
Support Systems
Support from family, friends or a support group can be invaluable.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management might include regular physical therapy, ongoing medication and lifestyle adjustments.
Myths and Facts About Bursitis
Common Misconceptions
One common myth is that bursitis only affects the elderly. In reality, it can affect anyone, especially those with repetitive joint use.
Evidence-Based Facts
Fact: Proper treatment and lifestyle changes can significantly improve symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Conclusion
Bursitis, while painful and inconvenient, is manageable with the right knowledge and approach. By understanding its causes, symptoms and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to treat and prevent it. Remember, listening to your body and seeking timely medical advice are key to overcoming bursitis and maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle.
FAQs
What is the main cause of bursitis?
Repetitive motion or prolonged pressure on a joint is the main cause of bursitis.
Can bursitis heal on its own?
Mild cases of bursitis can resolve on their own with rest and proper care, but more severe cases may require medical treatment.
What foods should be avoided with bursitis?
Foods that promote inflammation, such as sugary snacks, refined carbs and processed foods, should be limited.
Is bursitis the same as arthritis?
No, bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, while arthritis is the inflammation of the joints themselves.
How long does bursitis last?
The duration of bursitis can vary; it might last a few weeks to several months, depending on the cause and treatment.
