Table of Contents
Osteoarthritis, often referred to as the “wear and tear” arthritis, is a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide. Characterized by the degeneration of joint cartilage and underlying bone, osteoarthritis can lead to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of osteoarthritis and explore innovative solutions for managing this condition and achieving lasting relief.
What is Osteoarthritis?
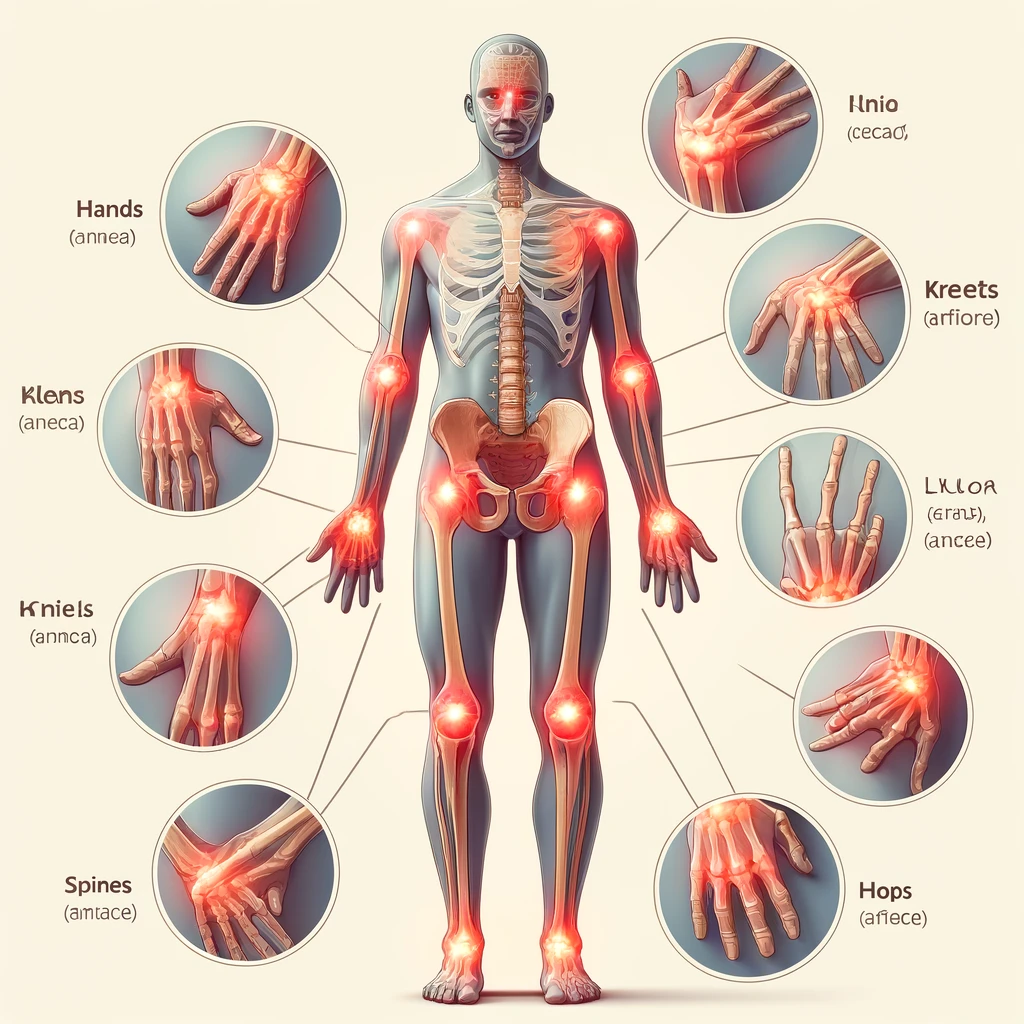
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage cushioning the ends of bones in your joints deteriorates over time. This condition can affect any joint but commonly occurs in the knees, hips, hands, and spine. The breakdown of cartilage results in pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the joint.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Early Signs
- Joint pain during or after movement
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after a period of inactivity
- Tenderness when applying pressure to the joint
Advanced Symptoms
- Loss of flexibility
- Grating sensation or sound when using the joint
- Bone spurs, or extra bits of bone, which may form around the affected joint
Diagnosing Osteoarthritis
Physical Examination
Doctors assess joint pain and functional limitations through physical examinations, evaluating the range of motion and areas of tenderness.
Imaging Tests
X-rays and MRIs are commonly used to visualize joint damage, cartilage loss, and bone changes associated with osteoarthritis.
Laboratory Tests
While there are no definitive blood tests for osteoarthritis, lab tests can help rule out other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Traditional Treatments for Osteoarthritis
Medications
NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Analgesics
Analgesics like acetaminophen can help manage pain without addressing inflammation.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy involves exercises tailored to strengthen muscles around the joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
Lifestyle Changes
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on weight-bearing joints, alleviating symptoms and slowing the progression of osteoarthritis.
Exercise
Regular exercise helps maintain joint function and manage pain. Low-impact activities like swimming and walking are often recommended.
Innovative Non-Surgical Treatments
Hyaluronic Acid Injections
Hyaluronic acid injections provide lubrication to the joint, improving mobility and reducing pain, particularly in knee osteoarthritis.
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting a concentration of a patient’s own platelets into the affected joint to promote healing and reduce inflammation.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy aims to regenerate damaged cartilage by injecting stem cells into the affected joint, potentially providing long-term relief.
Surgical Options for Osteoarthritis
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy involves a minimally invasive procedure to diagnose and treat joint problems, such as removing loose cartilage fragments.
Joint Replacement
Knee Replacement
In severe cases of knee osteoarthritis, knee replacement surgery can replace damaged joint surfaces with artificial components, relieving pain and restoring function.
Hip Replacement
Hip replacement surgery replaces the damaged hip joint with a prosthetic implant, significantly reducing pain and improving mobility.
Alternative Therapies for Osteoarthritis
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, the practice of inserting thin needles into specific points on the body, can help relieve osteoarthritis pain and improve joint function.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments may help align joints properly, reducing pain and improving function.
Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs, such as turmeric and ginger, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help manage osteoarthritis symptoms.
Diet and Osteoarthritis
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory compounds can help reduce inflammation and support joint health.
Foods to Avoid
Limiting the intake of processed foods, sugars, and trans fats can help prevent inflammation and manage symptoms.
Supplements
Supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin may support joint health and alleviate osteoarthritis symptoms.
Managing Osteoarthritis Pain
Pain Management Techniques
Techniques such as heat and cold therapy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and massage can help manage pain.
Role of Mind-Body Practices
Mind-body practices like yoga, tai chi and mindfulness meditation can help reduce pain perception and improve quality of life.
Exercise and Osteoarthritis
Types of Beneficial Exercises
Exercises such as strength training, flexibility exercises, and aerobic activities can help manage osteoarthritis symptoms and improve joint function.
Exercise Tips for Osteoarthritis Patients
Gradually increasing exercise intensity, using proper techniques, and listening to your body’s signals can help prevent injury and maximize benefits.
Living with Osteoarthritis
Daily Living Aids
Using assistive devices like canes, shoe inserts, and braces can make daily activities easier and reduce joint stress.
Coping Strategies
Adapting coping strategies such as pacing activities, practicing relaxation techniques and seeking support can improve quality of life.
Preventing Osteoarthritis Progression
Early Intervention
Early diagnosis and treatment can slow the progression of osteoarthritis and improve outcomes.
Long-Term Strategies
Long-term strategies such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying active and managing weight can help prevent the worsening of osteoarthritis symptoms.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis can significantly impact quality of life, but with the right approach, it is possible to manage symptoms and maintain an active, fulfilling lifestyle. By understanding the various treatment options, including innovative solutions, you can make informed decisions and find lasting relief from osteoarthritis.
FAQs
What are the early symptoms of osteoarthritis?
Early symptoms include joint pain, stiffness and tenderness during or after movement.
How is osteoarthritis diagnosed?
Osteoarthritis is diagnosed through physical exams, imaging tests like X-rays and MRIs, and laboratory tests to rule out other conditions.
What are innovative non-surgical treatments for osteoarthritis?
Innovative treatments include hyaluronic acid injections, PRP therapy and stem cell therapy.
Can diet affect osteoarthritis?
Yes, consuming anti-inflammatory foods and avoiding processed foods can help manage osteoarthritis symptoms.
What exercises are beneficial for osteoarthritis patients?
Beneficial exercises include strength training, flexibility exercises and low-impact aerobic activities like swimming and walking.