Table of Contents
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Proper management of this condition is crucial not only for maintaining daily quality of life but also for preventing potential complications. In this article, we will explore various effective strategies for managing diabetes, with a focus on maintaining stable blood glucose levels, adopting a healthy lifestyle and utilizing modern technology.
Understanding Diabetes
Before diving into management strategies, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of what diabetes is and how it affects your body. Diabetes occurs when your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar.
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: This type occurs when the body fails to produce insulin. It is often diagnosed in children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This is the most common type where the body does not use insulin properly. It is typically diagnosed in adults but is increasingly seen in children.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and usually disappears after giving birth, though it increases the mother’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes later.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Diabetes
Managing diabetes effectively requires comprehensive lifestyle changes that include diet, exercise and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels.
Diet and Nutrition: Eating Right with Diabetes
Effective diabetes management heavily relies on a well-planned diet. Understanding how different foods affect blood sugar is crucial for maintaining stable glucose levels. Here’s a more detailed exploration of dietary management for diabetes:
Comprehensive Carbohydrate Management
Understanding Carbs
Carbohydrates have the most direct impact on blood glucose levels. To manage diabetes effectively:
- Choose Complex Carbohydrates: Foods like whole grains, legumes, and fibrous vegetables are better because they have a lower glycemic index and provide sustained energy without causing abrupt blood sugar spikes.
- Read Labels: Being aware of added sugars and refined carbs in packaged foods can help you make better choices.
Glycemic Index and Load
- Glycemic Index (GI) measures how quickly food increases your blood sugar. Low-GI foods are preferable for stable blood sugar control.
- Glycemic Load (GL) takes into account the amount of carbohydrate in a serving as well as how quickly it raises your glucose levels. A low GL is generally better.
Protein and Fat in a Diabetes Diet
Role of Protein
- Stabilizes Blood Sugar: Including protein in your meals can help slow the absorption of carbohydrates, leading to more stable blood sugar levels.
- Sources: Opt for lean proteins like chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes.
Healthy Fats
- Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fats: Foods rich in these healthy fats can help improve blood cholesterol levels and reduce cardiovascular risks, which are higher in diabetic individuals. Examples include avocados, nuts, seeds and olive oil.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Particularly beneficial for heart health, these can be found in fish like salmon and trout, as well as in flaxseeds and walnuts.
Fiber: A Key Component
- Benefits: Fiber helps control blood sugar levels by slowing the breakdown of carbs and the absorption of sugar. This can help manage type 2 diabetes effectively.
- Sources: High-fiber foods include whole grains, legumes, fruits and vegetables.
Healthy Eating Patterns
Meal Planning
- Balanced Meals: Each meal should contain a good balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fat. This balance helps in mitigating blood sugar spikes and maintaining energy levels throughout the day.
- Portion Control: Eating appropriate portions is crucial to avoid overconsumption of calories and excessive blood sugar increases.
Consistent Meal Timing
- Regular Meals: Eating at regular times helps prevent drastic fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Skipping meals, especially breakfast, can lead to higher blood sugar levels later in the day.
Special Dietary Considerations
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can affect blood glucose levels and interfere with diabetes medications. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation and never on an empty stomach.
- Dining Out: When eating out, look for dishes that are lower in fat and sugar. Don’t hesitate to ask for meal modifications to suit your dietary needs.
Supplements and Vitamins
While most nutrients should come from the diet, some individuals might need supplements, especially if they have dietary restrictions or other health issues. Common supplements for those with diabetes include vitamin B12, vitamin D and magnesium, but always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
Exercise: A Pillar of Diabetes Management
Exercise is not just about burning calories; it’s a crucial element in managing diabetes. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helps manage weight and lowers the risk of heart disease.
The Importance of Aerobic Exercise
Types of Aerobic Exercise
- Brisk Walking: Easily accessible and effective. A 30-minute brisk walk five days a week can significantly impact blood sugar levels.
- Cycling: Low impact and enjoyable, suitable for all ages and helpful in building stamina and lower body strength.
- Swimming: Excellent for those with joint issues or who prefer a low-impact workout, it also helps improve overall body strength.
Benefits
- Improves Heart Health: Reduces cardiovascular risk, which is crucial since diabetes significantly increases heart disease risk.
- Enhances Insulin Utilization: Aerobic exercise helps the body use insulin more efficiently, often lowering the need for medication.
The Role of Resistance Training
Types of Resistance Training
- Weight Lifting: Builds muscle mass, which is beneficial because muscle tissue burns more calories than fat, even at rest.
- Bodyweight Exercises: Activities like push-ups, pull-ups, and leg squats that can be performed anywhere without special equipment.
- Resistance Bands: Offers versatility and different levels of resistance, which can help enhance strength without the need for heavy weights.
Benefits
- Improves Blood Glucose Control: Muscle gain from resistance training can improve glycemic control, as muscles use glucose for energy.
- Increases Bone Density: Particularly important for older adults, as diabetes can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Types of Exercises
- Yoga: Offers stress relief and improves flexibility, balance, and muscle tone.
- Tai Chi: A gentle form of exercise known for its rhythmic movements and is beneficial for balance, flexibility, and stress reduction.
Benefits
- Enhances Joint Mobility: Important for preventing stiffness and injury.
- Reduces Stress: High stress levels can cause blood sugar levels to spike; thus, these exercises can help maintain better glucose control.
Developing an Exercise Plan
Tailoring to Individual Needs
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Before starting any new exercise regimen, those with diabetes should consult with their healthcare team to tailor activities according to their current health status and risks.
- Start Slowly: For those new to exercise or returning after a break, it’s crucial to start slowly and increase intensity gradually to prevent hypoglycemia.
Monitoring Blood Sugar
- Before Exercise: Check blood sugar levels to ensure they are neither too low nor too high before starting to exercise.
- After Exercise: Monitoring after exercise is essential as physical activity can affect blood sugar levels for several hours afterward.
Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Life
- Take Short Walks: Frequent, shorter sessions of physical activity can be as beneficial as longer sessions. Consider walking during breaks at work.
- Use Technology: Fitness trackers can motivate and help track progress. They can be particularly useful for setting and sticking to exercise goals.
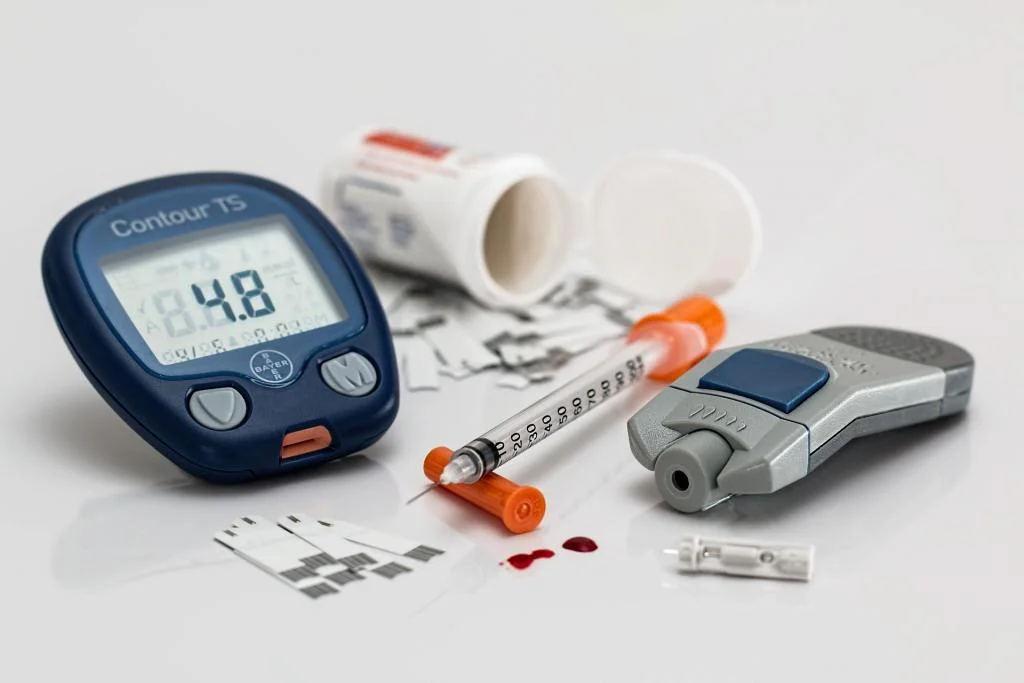
Monitoring and Medication
Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regular blood glucose monitoring is a cornerstone of diabetes management, allowing for adjustments in diet, exercise and medications.
Medication Adherence
Patients with diabetes may need medications or insulin therapy to manage their condition effectively. It is vital to adhere to prescribed medications and understand how they work.
Advances in Diabetes Technology
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Overview of CGMs
Continuous Glucose Monitors are revolutionary devices in diabetes management, providing real-time data on glucose levels. These devices involve a small sensor inserted under the skin that continuously measures glucose in the interstitial fluid.
How CGMs Enhance Diabetes Management
- Real-Time Feedback: CGMs offer instant feedback on glucose levels, allowing users to adjust their diet, exercise and insulin doses in real time.
- Trend Analysis: By tracking glucose levels over time, CGMs can help identify patterns and trends in blood sugar fluctuations, aiding in more informed management decisions.
- Alerts and Alarms: Most CGMs come with features that alert the user to high or low blood glucose levels, providing critical warnings that can help prevent hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic episodes.
Impact on Lifestyle
- Reduced Need for Fingersticks: For many users, CGMs can significantly reduce the number of daily fingersticks needed to monitor blood glucose levels, offering more comfort and convenience.
- Enhanced Confidence: Having continuous access to glucose data can increase a person’s confidence in managing their diabetes, reducing anxiety over unexpected glucose spikes or drops.
Insulin Pumps
Understanding Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are small, computerized devices that deliver insulin through a catheter placed under the skin. Unlike multiple daily insulin injections, pumps deliver insulin more consistently and can be adjusted based on the user’s current needs.
How Insulin Pumps Work
- Basal Rate: The pump continuously delivers small doses of insulin to maintain a steady level of insulin, known as the basal rate.
- Bolus Doses: When eating or if glucose levels are high, users can manually trigger the pump to deliver extra insulin, known as a bolus dose.
Benefits of Insulin Pumps
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: By mimicking the natural insulin release of a healthy pancreas, pumps can lead to better glucose control and reduced risk of long-term complications.
- Flexibility in Lifestyle: Insulin pumps allow for more flexibility in timing and size of meals, exercise and other activities.
- Decreased Insulin Stacking: Since pumps calculate the “on board” insulin, they can adjust bolus doses to avoid stacking extra insulin, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia.
Technological Integrations
- Link to CGMs: Many insulin pumps can now be integrated directly with CGMs, allowing for automatic adjustments in insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings.
- Smartphone Connectivity: Some newer models offer connectivity to smartphones for easier monitoring and control over insulin delivery, enhancing user convenience and control.
The Future of Diabetes Technology
Artificial Pancreas Systems
Looking forward, the development of artificial pancreas systems represents the next frontier in diabetes care. These systems combine CGM and insulin pump technologies to automatically adjust insulin delivery based on glucose levels, potentially minimizing the need for user intervention.
Increasing Accessibility
While these technologies offer substantial benefits, they are not yet universally accessible due to high costs and limited availability in some regions. Efforts are ongoing to improve accessibility and affordability, which could democratize the benefits of these advanced diabetes management tools.
Psychological and Social Support
Mental Health
Diabetes management can also take a psychological toll. Support from family, friends and support groups can help alleviate the stress associated with managing this chronic condition.
Education
Being informed about diabetes is critical. Consider attending workshops or seminars that focus on practical aspects of diabetes care.
Practical Tips for Everyday Management
- Stay Hydrated: Keeping well-hydrated is important for blood sugar control.
- Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Both smoking and excessive alcohol can worsen diabetes complications.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular visits with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor overall health and make necessary adjustments in the treatment plan.
Challenges in Diabetes Management
Despite advancements, managing diabetes remains a challenge due to its complex nature and the need for personalized treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Effective diabetes management involves a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, medication adherence, and the use of advanced technologies. By adopting these strategies, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy, active lives while minimizing the risk of complications. Remember, the key to successful diabetes management is a proactive approach to care, continuous education, and the support of a healthcare team.
FAQs
What is the most important aspect of managing diabetes?
The most crucial aspect of managing diabetes is maintaining stable blood sugar levels. This involves a combination of medication (if prescribed), dietary changes, regular exercise and monitoring blood glucose levels consistently.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
The frequency of blood sugar checks varies depending on individual circumstances and treatment plans. However, it’s generally recommended to check blood sugar levels multiple times a day, especially before meals, before bedtime and after exercise.
Is exercise important for managing diabetes?
Yes, exercise is crucial for managing diabetes. Regular physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, control weight, and reduce the risk of complications. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises.



