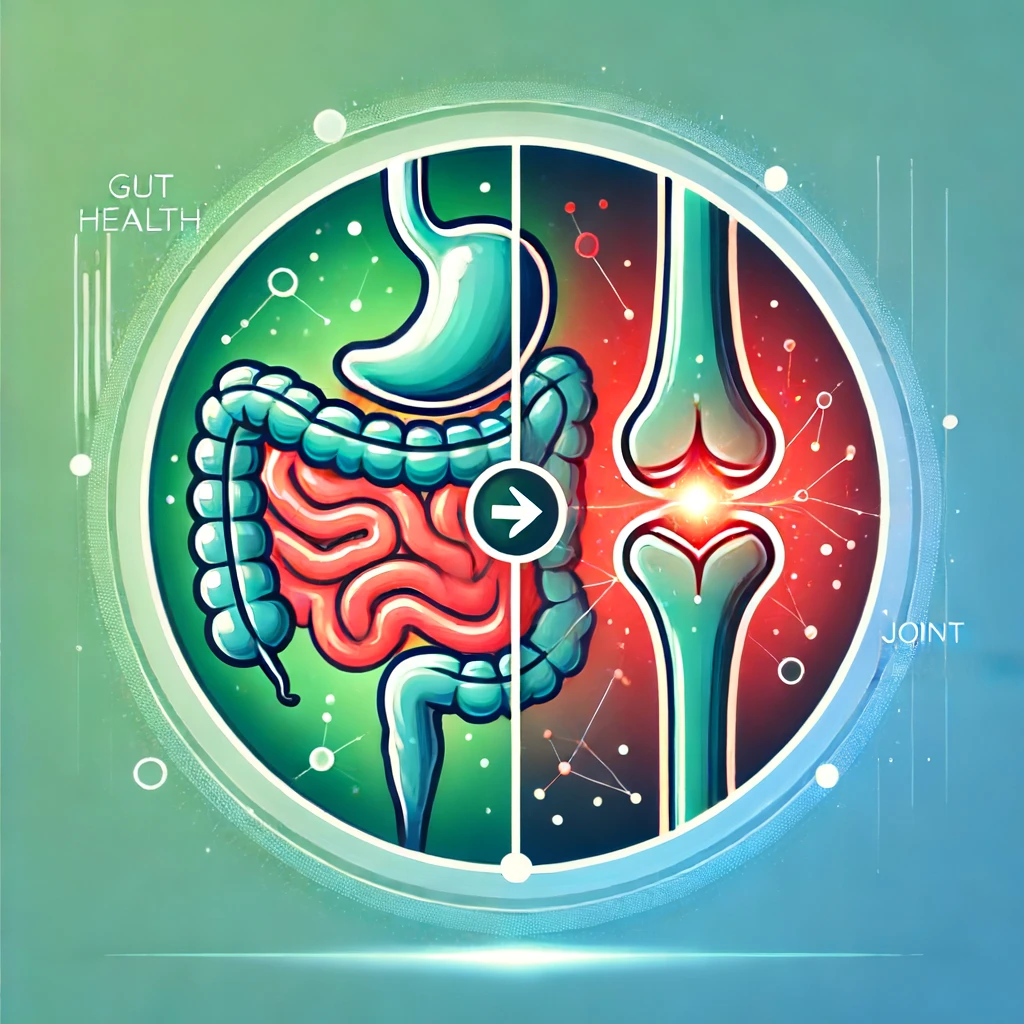
In recent years, research has increasingly highlighted the crucial role that gut health plays in overall wellness. An area that has garnered significant attention is the connection between gut health and joint inflammation. This link, often referred to as the gut-joint axis, suggests that imbalances in the gut can contribute to inflammatory conditions affecting the joints. Understanding this connection can provide new avenues for managing joint inflammation through dietary and lifestyle interventions. In this article, we’ll explore how gut health influences joint inflammation, what you can do to improve your gut health and how these changes can lead to better joint health.
Understanding Gut Health
Definition of Gut Health
Gut health refers to the balance of microorganisms living in the digestive tract, as well as the overall functionality of the gastrointestinal system. A healthy gut effectively digests food, absorbs nutrients and eliminates waste, all while maintaining a balanced microbiome.
Components of a Healthy Gut
Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota consists of trillions of bacteria, viruses and fungi. These microorganisms play a vital role in digestion, immune function, and overall health. A diverse and balanced microbiota is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut.
Gut Barrier
The gut barrier, or intestinal barrier, is a complex structure that prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream while allowing nutrients to pass through. This barrier helps protect the body from infections and inflammation.
What is Joint Inflammation?
Definition of Joint Inflammation
Joint inflammation, also known as arthritis, involves swelling, pain and stiffness in the joints. It can result from various causes, including autoimmune conditions, infections, or physical injuries.
Common Causes of Joint Inflammation
Arthritis
There are several types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, each with its own underlying mechanisms of joint inflammation.
Infections
Infections can cause acute joint inflammation, often leading to septic arthritis or reactive arthritis, where joint inflammation follows an infection elsewhere in the body.
Injuries
Physical injuries to the joints, such as sprains or fractures, can lead to inflammation as part of the body’s healing response.
The Gut-Joint Connection
How Gut Health Influences Inflammation
The gut plays a pivotal role in modulating the immune system. An imbalance in gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can trigger systemic inflammation, which may affect the joints.
The Role of the Immune System
The immune system constantly monitors the gut for pathogens. When the gut barrier is compromised, it can trigger an immune response that leads to inflammation in other parts of the body, including the joints.
Leaky Gut Syndrome and Inflammation
Leaky gut syndrome occurs when the intestinal barrier is damaged, allowing toxins and bacteria to enter the bloodstream. This can result in widespread inflammation and has been linked to various autoimmune conditions, including those affecting the joints.
Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Diseases
Microbiota Imbalance (Dysbiosis)
Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the gut microbiota, often characterized by a decrease in beneficial bacteria and an increase in harmful bacteria. This imbalance can contribute to the development of inflammatory diseases.
Impact on Autoimmune Conditions
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Research suggests that dysbiosis may play a role in the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Certain bacterial species in the gut have been associated with increased inflammation and autoimmunity.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Similarly, psoriatic arthritis, a condition characterized by joint inflammation and skin lesions, has been linked to changes in gut microbiota composition.
Diet’s Impact on Gut and Joint Health
Anti-Inflammatory Diets
Anti-inflammatory diets focus on foods that reduce inflammation and support gut health. These diets typically emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains and healthy fats while avoiding processed foods and sugars.
Foods to Include for Gut Health
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains, which support healthy digestion and feed beneficial gut bacteria.
- Fermented Foods: Like yogurt, kefir and sauerkraut, which are rich in probiotics.
- Healthy Fats: Such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and flaxseed, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
Foods to Avoid
- Processed Foods: High in sugars and unhealthy fats that can promote inflammation.
- Artificial Additives: Such as preservatives and colorings that may disrupt gut health.
- Excessive Alcohol: Can harm the gut lining and promote dysbiosis.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are live bacteria that provide health benefits when consumed. They can help restore balance to the gut microbiota and support overall gut health.
Benefits of Probiotics for Joint Inflammation
Probiotics may help reduce inflammation by enhancing the gut barrier function and modulating the immune system. Some studies suggest that specific strains of probiotics can reduce symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
What Are Prebiotics?
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria. They promote the growth of probiotics and support a healthy gut environment.
How Prebiotics Support Gut Health
Prebiotics help maintain a healthy gut microbiota by providing nutrients that beneficial bacteria need to thrive. Common sources include garlic, onions, bananas, and whole grains.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Gut and Joint Health
Stress and Its Impact
Chronic stress can negatively impact both gut health and joint inflammation. Stress hormones can alter gut microbiota composition and weaken the gut barrier.
Sleep Quality
Poor sleep can exacerbate both gut and joint health issues. Lack of sleep has been linked to increased inflammation and alterations in gut microbiota.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity supports both gut health and joint function. Exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce inflammation, and promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Signs Your Gut Health May Be Affecting Your Joints
Digestive Symptoms
Frequent digestive issues, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea, can indicate poor gut health, which may be linked to joint inflammation.
Unexplained Joint Pain
If you experience joint pain without an apparent cause, it could be related to underlying gut health issues.
Fatigue and Mood Changes
Chronic fatigue and mood swings can also be signs of gut-related problems that might be affecting your joints.
Testing and Diagnosing Gut Issues
Common Gut Health Tests
Tests such as stool analysis, breath tests, and blood tests can help diagnose gut health issues and guide treatment plans.
How They Relate to Joint Health
Identifying and addressing gut health issues can lead to improvements in joint inflammation and overall health.
Natural Remedies for Improving Gut Health
Herbal Supplements
Herbs like ginger, turmeric, and peppermint can support gut health and reduce inflammation. They may be used as supplements or in culinary preparations.
Dietary Changes
Adopting a diet rich in anti-inflammatory and gut-friendly foods can significantly improve gut health and reduce joint inflammation.
Hydration
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining healthy digestion and supporting overall gut function.
Medical Treatments for Gut-Related Joint Inflammation
Medications
Certain medications, such as anti-inflammatories and antibiotics, may be used to treat both gut issues and joint inflammation. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any medication.
Therapies and Procedures
In some cases, therapies such as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) or procedures to repair the gut barrier may be recommended.
Managing Joint Inflammation through Gut Health
Personalized Nutrition
Working with a nutritionist to develop a personalized diet plan can help address both gut health and joint inflammation effectively.
Gut-Directed Therapies
Therapies focused on improving gut health, such as probiotic supplements or dietary adjustments, can lead to significant improvements in joint health.
Future Research and Developments
New Insights into the Gut-Joint Axis
Ongoing research continues to uncover the complex interactions between the gut and joints, offering new insights into potential treatments and preventive measures.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
Innovative treatments, such as targeted probiotic therapies and advanced gut health diagnostics, are on the horizon, promising better management of gut-related joint inflammation.
Conclusion
The connection between gut health and joint inflammation highlights the importance of a holistic approach to managing inflammatory conditions. By focusing on improving gut health through diet, lifestyle changes, and appropriate treatments, you can significantly impact your joint health and overall well-being. Stay informed, work with healthcare professionals and embrace a proactive approach to managing your health.
FAQs
Can improving gut health reduce joint pain?
Yes, improving gut health can reduce systemic inflammation, which may alleviate joint pain.
What foods should I avoid to maintain healthy joints?
Avoid processed foods, excessive sugars and artificial additives that can promote inflammation.
How long does it take for diet changes to impact joint health?
It may take several weeks to months to see significant improvements, but some individuals notice changes sooner.
Are there specific probiotics that help with joint inflammation?
Certain probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, have shown promise in reducing inflammation.
How can I tell if my gut health is affecting my joints?
Signs include digestive issues, unexplained joint pain and systemic symptoms like fatigue and mood changes.