
Table of Contents
Living with diabetes doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With the right knowledge and tools, you can take charge of your health and effectively manage your condition. In this blog post, we’ll explore 10 practical tips to help you navigate the challenges of diabetes management and live your best life.
I. Understanding Diabetes
A. What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body uses glucose (sugar) from the food you eat. It occurs when the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin or when the body can’t effectively use the insulin it produces.
B. Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, including Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Each type has its own causes, risk factors, and management strategies.
C. Risk Factors for Diabetes
Risk factors for diabetes include genetics, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and certain medical conditions. Understanding these risk factors can help you take preventive measures and manage your condition effectively.
II. Healthy Eating Habits

A. Balanced Diet for Diabetics
A balanced diet for diabetes includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Focus on portion control and moderation to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
B. Meal Planning and Portion Control
Meal planning involves choosing healthy foods, balancing carbohydrates with protein and fat, and monitoring portion sizes. This helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes overall health.
C. Importance of Monitoring Carbohydrate Intake
Monitoring carbohydrate intake is crucial for diabetics as carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. Learn to count carbs and make informed food choices.
III. Regular Physical Activity

A. Benefits of Exercise for Diabetes
Exercise offers numerous benefits for diabetics, including improved blood sugar control, weight management, increased insulin sensitivity, and reduced risk of complications.
B. Types of Exercise for Diabetes Management
Both aerobic exercise (such as walking, cycling, or swimming) and strength training (using weights or resistance bands) are beneficial for diabetes management. Aim for a combination of both types of exercise.
C. Developing a Sustainable Exercise Routine
Find activities you enjoy and can incorporate into your daily routine. Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Consistency is key to reaping the benefits of exercise.
IV. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
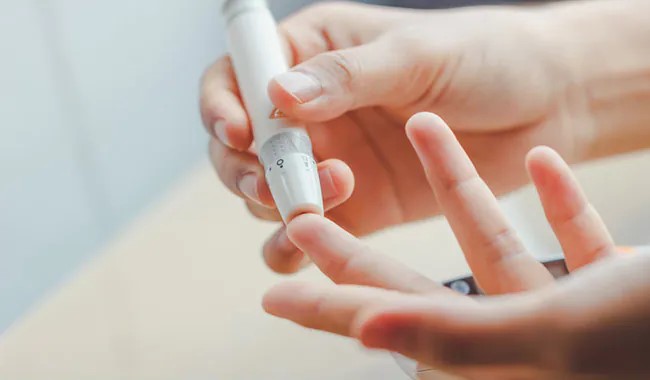
A. Importance of Regular Blood Sugar Checks
Regular blood sugar checks are essential for monitoring your diabetes control and making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication adjustments.
B. Types of Monitoring Devices
There are various blood glucose monitoring devices available, including glucometers, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and flash glucose monitoring systems. Choose the device that best suits your needs and lifestyle.
C. Interpreting Blood Sugar Readings
Learn to interpret your blood sugar readings and understand how different factors (such as food, exercise, stress, and medication) affect your blood sugar levels. Work with your healthcare team to set target ranges for your blood sugar readings.
V. Medication Management
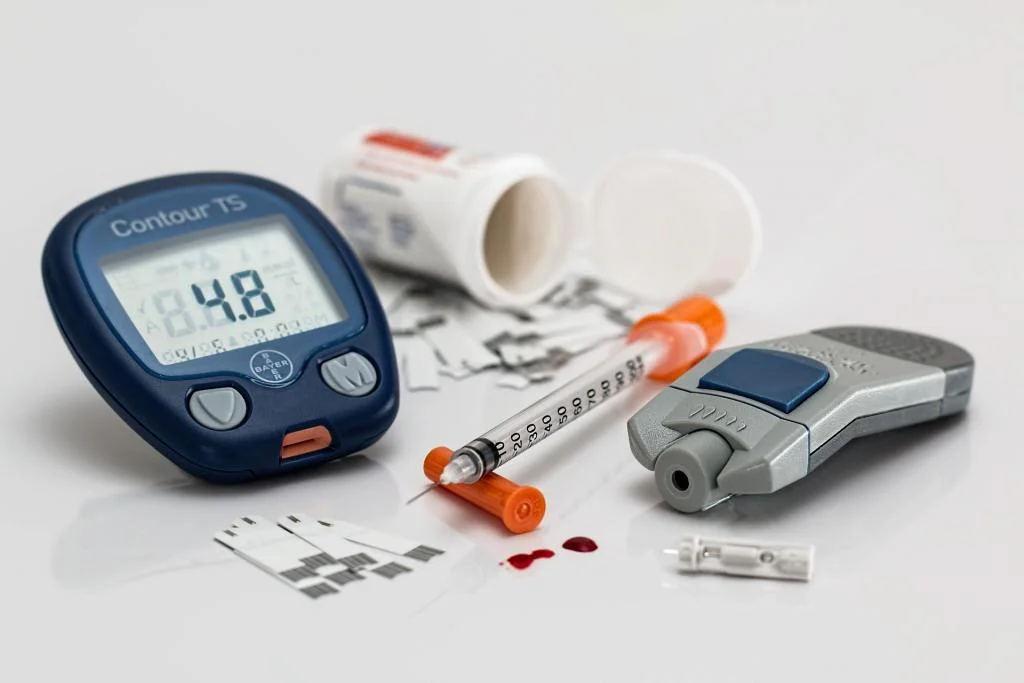
A. Importance of Taking Medications as Prescribed
Taking medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider is crucial for managing diabetes effectively and preventing complications.
B. Types of Diabetes Medications
There are several classes of diabetes medications, including insulin, oral medications, and injectable medications. Each type of medication works differently to lower blood sugar levels.
C. Dealing with Side Effects and Adjusting Dosages
Be aware of potential side effects of diabetes medications and communicate any concerns with your healthcare provider. Adjusting dosages or trying different medications may be necessary to achieve optimal diabetes control.
VI. Stress Management

A. How Stress Impacts Blood Sugar Levels
Stress can affect blood sugar levels by triggering the release of hormones that raise blood sugar levels. Learning to manage stress effectively is essential for diabetes management.
B. Stress-Relief Techniques for Diabetics
Practice stress-relief techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness to reduce stress and promote relaxation.
C. Incorporating Relaxation into Daily Routine
Make time for relaxation and self-care activities in your daily routine. Prioritize activities that bring you joy and help you unwind, such as spending time with loved ones, enjoying hobbies, or taking nature walks.
VII. Building a Support System

A. Importance of Having a Support System
Having a strong support system can provide emotional encouragement, practical assistance, and accountability in managing your diabetes.
B. Involving Family and Friends in Diabetes Management
Educate your family and friends about diabetes and how they can support you in managing your condition. Share your goals, challenges, and achievements with them.
C. Joining Diabetes Support Groups
Consider joining diabetes support groups or online communities where you can connect with others who understand what you’re going through. Sharing experiences and tips with peers can be empowering and motivating.
VIII. Regular Medical Check-Ups

A. Importance of Regular Visits to Healthcare Providers
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your diabetes control, assessing your overall health, and addressing any concerns or complications.
B. Recommended Tests for Diabetics
Your healthcare provider may recommend specific tests and screenings for diabetes complications, such as eye exams, foot exams, kidney function tests, and cholesterol tests.
C. Developing a Diabetes Management Plan with a Healthcare Team
Work collaboratively with your healthcare team to develop a personalized diabetes management plan that addresses your unique needs, goals, and preferences.
IX. Setting Realistic Goals
A. Establishing Long-Term and Short-Term Goals
Set achievable long-term and short-term goals for managing your diabetes, such as reaching target blood sugar levels, losing weight, or increasing physical activity.
B. Celebrating Achievements Along the Way
Celebrate your progress and achievements along the way, no matter how small. Recognizing your efforts and successes can boost your confidence and motivation.
C. Adjusting Goals as Needed Based on Progress
Be flexible and willing to adjust your goals as needed based on your progress, setbacks, and changing circumstances. Focus on continuous improvement and growth.
X. Educating Yourself about Diabetes

A. Resources for Learning More about Diabetes
Take advantage of educational resources, such as books, websites, podcasts, and seminars, to deepen your understanding of diabetes and stay informed about the latest developments in diabetes management.
B. Staying Up-to-Date on the Latest Research and Guidelines
Stay up-to-date on the latest research findings, treatment guidelines, and recommendations for diabetes management. Knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
C. Sharing Knowledge with Others in the Diabetes Community
Share your knowledge and experiences with others in the diabetes community. By sharing information and supporting each other, we can all learn and grow together.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, effective diabetes management requires a holistic approach that encompasses healthy eating, regular exercise, proper medication management, stress reduction, social support, regular medical check-ups, goal setting, and continuous education. By following these 10 practical tips, individuals with diabetes can take control of their health and improve their quality of life.
By implementing these practical tips for better diabetes management into your daily life, you can take control of your health and thrive despite the challenges of living with diabetes. Remember, you’re not alone on this journey, and with the right support and resources, you can live a full and fulfilling life with diabetes.
FAQs:
Can diabetes be cured completely?
While there is currently no cure for diabetes, it can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes and medications.
Is it safe for diabetics to exercise?
Yes, regular physical activity is important for diabetics as it helps control blood sugar levels and improves overall health. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen.
What brings down blood sugar immediately?
If you need to quickly lower your blood sugar, drinking water and going for a brisk walk can help. Additionally, consuming a small portion of fast-acting carbohydrates, like glucose tablets or fruit juice, can bring your blood sugar levels back to a safer range. However, it’s essential to monitor your blood sugar closely and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
What is a safe sugar level?
A safe blood sugar level typically falls between 70 and 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) before meals and less than 180 mg/dL about two hours after eating. However, individual targets may vary, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine your specific target range based on factors such as age, overall health, and diabetes management goals.


